Choosing the right wireless microphone frequency can feel overwhelming. However, understanding the basics is crucial to achieving smooth, uninterrupted sound. Whether you’re setting up for a concert, conference, or church service, knowing how to select the correct frequencies will improve your audio quality.
‘’To choose wireless microphone frequencies, avoid crowded bands like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. Check local frequency regulations, ensure compatibility with other devices, and choose UHF or VHF bands for better range. Monitor for interference and adjust frequencies accordingly.’’
In this article, we will discuss about ‘’how to choose wireless microphone frequencies?’’
Why Choosing The Right Frequency Matters?
Using the wrong frequencies can lead to interference, noise, and poor sound quality. In a professional setting, this can result in embarrassing dropouts or disruptions. By selecting the right frequency, you’ll reduce the chances of signal interference and ensure your microphone system works seamlessly.
Understanding Frequency Bands
What Are Frequency Bands?
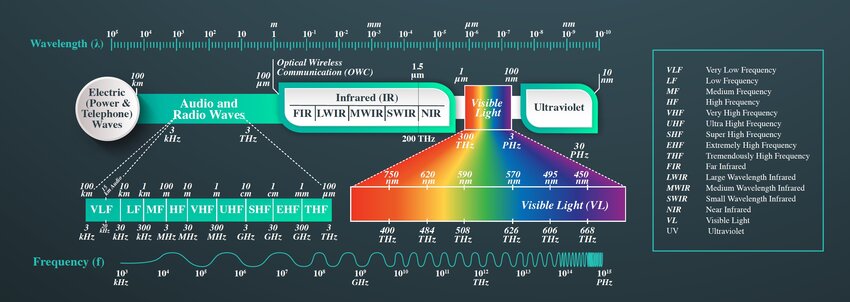
Frequency bands are ranges of electromagnetic frequencies that wireless devices use to transmit sound. In the context of wireless microphones, frequency bands help determine how well the microphone transmits sound without interference.
Vhf (Very High Frequency):
VHF operates between 30 MHz and 300 MHz. While VHF was widely used in the past, it’s now less common due to limited channel availability and susceptibility to interference. However, it can still work well in some rural areas with low RF (radio frequency) congestion.
Uhf (Ultra High Frequency):
UHF operates between 300 MHz and 3 GHz and is by far the most common range for wireless microphones today. It offers more available channels and better signal strength over longer distances. UHF is ideal for professional-grade performances but can be prone to interference from nearby TV broadcasts.
2.4 Ghz And Other Digital Frequencies:
These are often used in consumer-grade wireless systems and offer a simple plug-and-play solution. The 2.4 GHz band is globally available, making it an appealing choice for international use. However, this band can be crowded with Wi-Fi networks, Bluetooth devices, and other electronics.
Ism Bands:
The Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM) bands (including 900 MHz, 2.4 GHz, and 5.8 GHz) are designated for unlicensed use. While this means they are more accessible, it also means more competition for clear channels, especially in areas with many devices.
Also Read: How To Connect Multiple Microphones? – Comprehensive Guide Of 2024!
Factors To Consider When Choosing Frequencies:
Local Frequency Regulations:
Check your country’s frequency regulations to avoid restricted bands. Some frequencies are reserved for government, military, or emergency services, and using them could lead to fines. Ensure your microphone operates on legal and available frequencies in your region.
Interference:
Choose frequencies with minimal interference from Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or other wireless devices. UHF bands typically offer less interference compared to VHF. Scanning for open frequencies in your location helps you avoid disruptions caused by nearby electronic equipment or radio signals.
Frequency Range:
Evaluate the range of the wireless microphone’s frequency band. UHF bands often provide better range and signal strength, making them ideal for larger venues. For smaller indoor environments, VHF bands can be a more cost-effective choice with decent range.
Number Of Microphones:
Consider how many wireless microphones you’ll be using simultaneously. Multiple microphones may require different frequency channels to avoid cross-talk or interference. Choosing a frequency band that allows multiple devices to operate without overlap is crucial for seamless performance.
Venue Environment:
The venue’s structure can impact wireless frequency performance. Metal walls, electronic devices, and physical obstructions can cause signal dropouts. UHF frequencies tend to penetrate better in complex environments, while VHF frequencies may struggle in crowded or challenging venues.
Also Read: How Heavy Is A Microphone? – Ultimate Guide Of 2024!
How Frequency Interference Affects Performance
What Causes Interference?
Interference occurs when two devices operate on the same frequency. This can happen if your microphone is using a frequency that overlaps with local TV stations, Wi-Fi networks, or other wireless microphones.
How To Avoid Interference?
The best way to avoid interference is by selecting a frequency that’s not being used by other nearby devices. Many modern wireless microphone systems offer automatic frequency selection to help you find a clear channel.
Wireless Frequency Management Tips:
Best Practices For Frequency Management:
- Always scan for available frequencies before use.
- Assign unique frequencies to each microphone.
- Monitor for interference during performances and be ready to switch frequencies if needed.
How To Monitor Frequencies During Performances?
Use a frequency management system or app to monitor your microphones in real-time and make quick adjustments if necessary.
What Is The Best Frequency For Wireless Mics?
The best frequency depends on your location and environment. UHF frequencies between 470-698 MHz are commonly preferred for professional use due to their stability and range. However, always check local regulations and available frequencies in your area.
How Do I Match The Frequency Of My Wireless Microphone?
To match frequencies, first, set your wireless microphone and receiver to the same frequency. Most modern systems offer an auto-scan feature to help you find available frequencies. After selecting, confirm both devices are synchronized for optimal performance.

Which Frequency Is Best For A Microphone?
The UHF band (470-698 MHz) is considered the best for wireless microphones due to its lower interference rates and broader range. It’s ideal for professional use, especially in environments with multiple wireless devices.
Also Read: How To Detect Hidden Camera Or Microphone? – All You Must Know!
Is Uhf Or Vhf Better For Wireless Mics?
UHF is generally better for wireless mics, offering more available frequencies, less interference, and greater range. VHF is more affordable but is prone to interference, making it less suitable for professional environments with heavy wireless traffic.
What Frequency Is Banned For Wireless Microphones?
In the U.S., the 600 MHz band (614-698 MHz) is banned for wireless microphones due to its repurposing for mobile broadband. Always check local laws, as frequencies can vary by region.
Should I Use Vhf Or Uhf?
UHF is recommended for most professional applications due to its superior range and reduced interference. VHF may be suitable for smaller setups, but it’s more vulnerable to interference from other devices and environmental factors.
How To Choose The Best Wireless Microphone?
Choose based on frequency range, interference resistance, and your environment. UHF systems are better for professional use, while VHF works for smaller settings. Consider digital vs. analog and the number of microphones you plan to use simultaneously.
Scanner To Pick Wireless Microphone Frequency?
Many wireless microphone systems include an auto-scan feature that identifies the best available frequency. External frequency scanners or apps can also help detect clear channels, especially useful for large productions with multiple devices.
Wireless Microphone Frequency Range?
The typical frequency range for wireless microphones is between 174 MHz and 216 MHz (VHF) or 470 MHz to 698 MHz (UHF). Some systems also use the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz bands, often shared with Wi-Fi and other devices.
How To Set Wireless Microphone Frequencies?
Most wireless microphone systems have an auto-scan feature to select the best available frequency. For manual setup, tune both the microphone and receiver to the same frequency, ensuring it doesn’t conflict with nearby devices.
Also Read: How Do You Spell Microphone? – Read Now!
What Wireless Microphone Frequencies Are Illegal?
Frequencies in the 600 MHz band (614-698 MHz) are illegal for wireless microphone use in the U.S. and some other regions. Always check local regulations, as using restricted frequencies can lead to fines or equipment confiscation.
Is There A Trick/Guide To Selecting Frequencies For Many Wireless Mics?
To avoid interference, assign unique frequencies to each microphone. Use frequency coordination tools or apps, and ensure no overlap. Scanning available channels before your event helps ensure interference-free operation across multiple devices.
Are My Wireless Microphones Still Legal?
Check the operating frequency of your wireless microphones. In the U.S., frequencies within the 600 MHz range (614-698 MHz) are banned for microphone use. If your microphones fall within this range, they are no longer legal to operate.
FAQ’s:
1. What Happens If I Use The Wrong Frequency?
You could experience interference, poor sound quality, or even face legal consequences for violating local regulations.
2. Can I Use The Same Frequency For Multiple Microphones?
No, each microphone needs a unique frequency to avoid interference.
3. How Do I Know If My Wireless Microphone Frequency Is Legal?
Check with local frequency regulations or the FCC for legal guidelines.
4. What’s The Difference Between Analog And Digital Wireless Systems?
Digital systems offer more efficient use of bandwidth and are less prone to interference compared to analog systems.
5. Do Wireless Microphone Frequencies Change Over Time?
Yes, regulations and available bands can change, so it’s essential to stay updated.
Final Words:
Choosing wireless microphone frequencies involves understanding frequency bands, avoiding interference, and ensuring legal compliance. Opt for UHF frequencies for professional use, as they offer better range and stability. Always scan for available channels and coordinate frequencies if using multiple devices. By following these guidelines, you can ensure optimal performance and seamless audio quality for your events.
Also Read:
